Coder is a Remote Cloud Development Platform
Introduction:
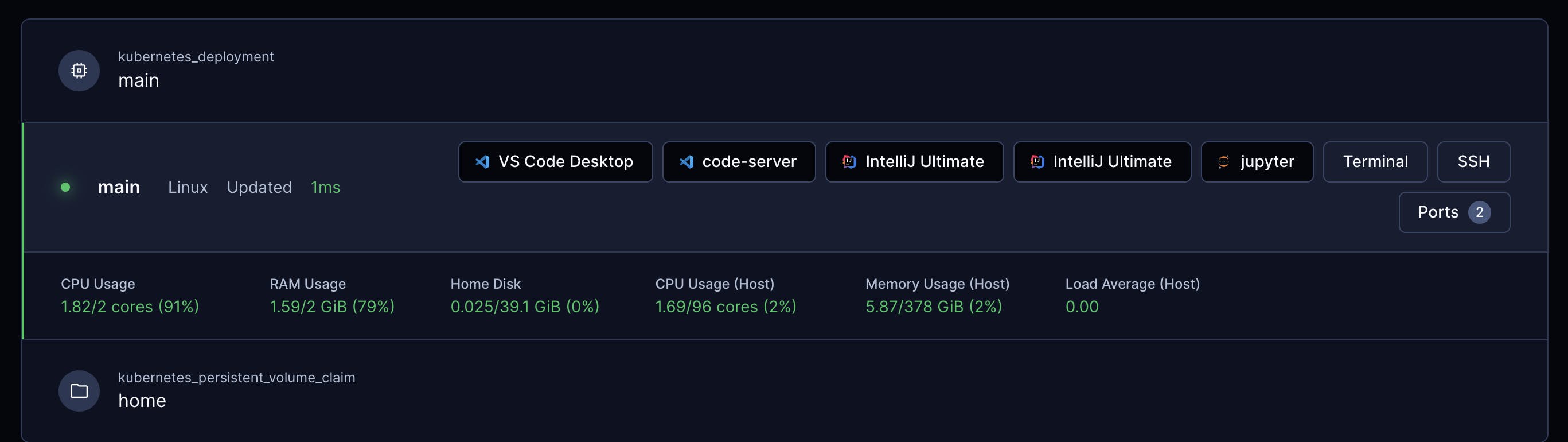
The Coder Remote platform is a self-hosted remote development platform that shifts software development from local machines to the cloud. It allows developers to onboard new team members in minutes and build code on powerful servers while keeping source code and data secure behind their firewall. The platform is designed to eliminate developer onboarding and make developers more productive than manually setting up development environments on their local machines/laptops.
The platform is also integrated with JetBrains Gateway, allowing developers to run their favorite JetBrains IDE remotely with seamless integration.
Scope of Article
This article will go through how to build up Coder V2 Enterprise Infrastructure on an Air-Gapped Google Cloud GKE cluster using HashiCorp Terraform
Before you Begin
Create a project in the Google Cloud Console and set up billing on that project. Any examples in this guide will be part of the GCP “always free” tier.
Please refer to this page for information on how to set up a Service Project, a Shared VPC Network, and Firewall Rules with the necessary IAM permissions for your service account and user account.
https://cloud.google.com/kubernetes-engine/docs/how-to/cluster-shared-vpc
Install Terraform (This article is written in Terraform v1.3.5)
First, authenticate with GCP. The easiest way to do this is to run
gcloud auth application-default login, if you already have gcloud installed. If you don't already have it, you can install it from here.
Implemenation Steps:
Here is the Terraform Tree Structure Looks like for the overall implementation:
terraform:
├── <prod/dev>
└── coder
└── helm
└── coder_helm_2.1.5.tgz ## download specic version Helm
└── templates
└── values.yanl
└── backend.tf
└── cloud-sql-proxy.yaml
└── cloud-sql-service-account.yaml
└── default-backend-config.yaml
└── helm.tf
└── namespace.tf
└── provider.tf
└── vpn-timeout.yaml
Step 1 - Coder backend database - Cloud SQL
https://harishgaggar.hashnode.dev/google-cloud-sql-database-using-terraform
Step 2 - Setting up GKE Cluster
https://harishgaggar.hashnode.dev/terraform-shared-vpc-gke-cluster-on-google-cloud
Step 3 - Setting up Coder
3.1 Download Helm
https://artifacthub.io/packages/helm/coder-v2/coder
In this article, we have downloaded latest version as of Oct 1, 2023 - coder_helm_2.1.5.tgz
3.2 provider.tf
terraform:
├── <prod/dev>
└── coder
└── provider.tf
Create a Terraform configuration file to configure the required version of Terraform and the required providers to connect with Google Cloud
# Declare the connection to the google provider with Terraform required version
terraform {
required_providers {
google = {
version = var.google_provider_version
}
}
required_version = var.terraform_version
}
provider "google" {
project = var.project_id
region = var.region
impersonate_service_account = "<SERVICE_ACCOUNT_NAME>@<PROJECT_ID>.iam.gserviceaccount.com"
}
Note: This article does not cover how to use Google Cloud Service Account impersonation in your Terraform code. For the production use case, we recommend using a service account access token in the provider block.
3.3 backend.tf
terraform:
├── application
└── cluster
└── backend.tf
Using Google Cloud Storage bucket to store Terraform state file.
terraform {
backend "gcs" {
bucket = "coder-tfstate"
prefix = "terraform/state/coder"
}
}
Note*: Before executing above, please create GCS bucket "coder-state"*
3.4 Create Coder DB Cloud SQL service account and proxy
terraform:
├── <prod/dev>
└── coder
└── cloud-sql-proxy.yaml
└── cloud-sql-service-account.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: cloud-sql-service-account
# cloud-sql-proxy.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: cloud-sql-service-account
#cloud-sql-service-account.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: cloud-sql-proxy
namespace: coder
labels:
app: cloud-sql-proxy
spec:
ports:
- port: 5432
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 5432
selector:
app: cloud-sql-proxy
sessionAffinity: None
type: ClusterIP
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
annotations:
deployment.kubernetes.io/revision: "1"
generation: 1
name: cloud-sql-proxy
namespace: coder
spec:
progressDeadlineSeconds: 600
replicas: 1
revisionHistoryLimit: 10
selector:
matchLabels:
app: cloud-sql-proxy
strategy:
rollingUpdate:
maxSurge: 25%
maxUnavailable: 25%
type: RollingUpdate
template:
metadata:
creationTimestamp: null
labels:
app: cloud-sql-proxy
spec:
serviceAccountName: cloud-sql-service-account
automountServiceAccountToken: false
containers:
- command:
- /cloud_sql_proxy
# Connect to your Google Cloud Cloud SQL Console and check DB Instance Detail
- -instances=<PLEASE ENTER DB INSTANCE>=tcp:#.#.#.#:5432
image: gcr.io/cloudsql-docker/gce-proxy:latest
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
name: cloud-sql-proxy
ports:
- containerPort: 5432
name: tcp-5432
protocol: TCP
resources: {}
securityContext:
allowPrivilegeEscalation: true
privileged: false
readOnlyRootFilesystem: false
runAsNonRoot: true
3.5 Create namespace
terraform:
├── <prod/dev>
└── coder
└── namespace.tf
// export access token for auth into cluster
data "google_client_config" "default" {}
// k8s provider declaration & auth
provider "kubernetes" {
config_path = "~/.kube/config"
}
// k8s resource definitions for coder
resource "kubernetes_namespace" "coder-ns" {
metadata {
name = "coder"
}
}
3.6 Setting up values.yaml
terraform:
├── <prod/dev>
└── coder
└── templates
└── values.yanl
coder:
env:
- name: CODER_PG_CONNECTION_URL
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
# Please create GKE secerts for Cloud SQL DB URL
name: coder-db-url
key: url
- name: CODER_ACCESS_URL
value: "https://#################.com"
- name: CODER_WILDCARD_ACCESS_URL
value: "*.################.com"
# Please create Google OAuth Client setup, Refer https://support.google.com/cloud/answer/6158849?hl=en
- name: CODER_OIDC_ISSUER_URL
value: "https://accounts.google.com"
- name: CODER_OIDC_EMAIL_DOMAIN
value: "##########.com"
- name: CODER_OIDC_CLIENT_ID
valueFrom:
# Please create GKE secrets for Client ID that generated during OAuth setup (In step above)
secretKeyRef:
name: client-id
key: url
- name: CODER_OIDC_CLIENT_SECRET
valueFrom:
# Please create GKE secrets for Client secret that generated during OAuth setup (In step above)
secretKeyRef:
name: client-secret
key: url
- name: CODER_VERBOSE
value: "true"
# Disable telemetry
- name: "CODER_TELEMETRY_ENABLE"
value: "false"
# Disable automatic update checks
- name: "CODER_UPDATE_CHECK"
value: "false"
# Only use relayed connections
- name: "CODER_DERP_SERVER_STUN_ADDRESSES"
value: ""
image:
# Since this is AirGap installation, please docker image in premise and upload to your Artifact or Google Container Registry
repo: "gcr.io/<GCP_PROJECT-ID>/<DOCKER-IMAGE-CODER-WITH-TERRAFORM>"
pullPolicy: Always
tag: "v2.1.5"
# Helm service will create Node Service Load balancer
service:
enable: true
type: NodePort
annotations:
cloud.google.com/backend-config: '{"default": "vpn-policy"}'
# Helm create Ingress rules that define how the incoming external traffic is routed to service IP above
ingress:
enable: true
className: ""
host: "#################.com"
wildcardHost: "*.###################.com"
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.global-static-ip-name: ext-ip
kubernetes.io/ingress.allow-http: "false"
# Please create GKE secret for your URL SSL cert and key
tls:
enable: true
secretName: "tls-secret"
wildcardSecretName: "tls-secret"
# Redirecting Coder service to control plane GKE node pool to keep it sepereate from user pod traffic
nodeSelector:
tier: control-plane
tolerations:
- key: "tier"
operator: "Equal"
value: "control-plane"
effect: "NoSchedule"
# Running 3 Coder services
replicaCount: 3
3.8 Kubectl Apply
Please apply each yaml file one at a time in order specified above. Example:
kubectl apply -f ./cloud-sql-proxy.yaml
* kubectl apply is a command used to manage applications through files defining Kubernetes resources
3.9 Apply helm.tf
// helm provider declaration
provider "helm" {
kubernetes {
config_path = "~/.kube/config"
}
}
// pull down coder helm chart & install it
resource "helm_release" "coder-chart" {
name = "coder"
chart = "./helm/coder_helm_2.1.5.tgz"
namespace = "coder"
values = [
"${file("./templates/values.yaml")}"
]
}
3.10 Apply Terraform
# Initialize environment
### Step 1. Terraform init
Follow conventional terraform workflow to build this solution.
You will be prompted for required variables.
Alternatively, you may create a `vars.tfvars` file and
apply the `-var-file=vars.tfvars` flag.
Initialize the terraform environment.
```
terraform init
```
### Step 2. Terraform plan
Plan the terraform solution.
```
terraform plan
```
or
```
terraform plan -var-file=vars.tfvars
```
### Step 3. Terraform apply
Apply the terraform solution.
```
terraform apply
```
or
```
terraform apply -var-file=vars.tfvars
```
Please check if all Coder services running fine by connecting Coder GKE Cluster and running kubectl commands:
kubectl get pods -n=coder
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
cloud-sql-proxy-################ 1/1 Running 0 1d
coder-################ 1/1 Running 0 1d
coder-################ 1/1 Running 0 1d
coder-################ 1/1 Running 0 1d
Connect to your Coder URL
Please refer to https://coder.com/docs/v2/latest/install/kubernetes for further information. If any questions or suggestions, please feel free to comment.

